Contract Verification
To promote transparency, it is considered best practice to verify all deployed contracts on the Core blockchain. While there are several ways to achieve contract verification, we recommend using Core's official verification tool, Core Scan, for optimal reliability. This document guides you through the most commonly used methods for contract verification: the Core Scan web tool, the Core REST API, and the Hardhat Verification plugin.
Ensure that your smart contract complies with the Solidity Support Guidelines by Core. To meet these guidelines, set the evmVersion parameter to shanghai within the Solidity compiler settings.
Web Verification via Core Scan
Web verification is the most commonly used method for smart contract verification. After deploying your smart contract onto the Core blockchain, you can use its source code to verify it on the Core Scan.
- Navigate to the Core Scan website.
- Search for the contract by address on Core Scan. Simply paste the contract address in the search bar on the website.
- After locating the contract, select the Contract tab and click Verify and Publish.
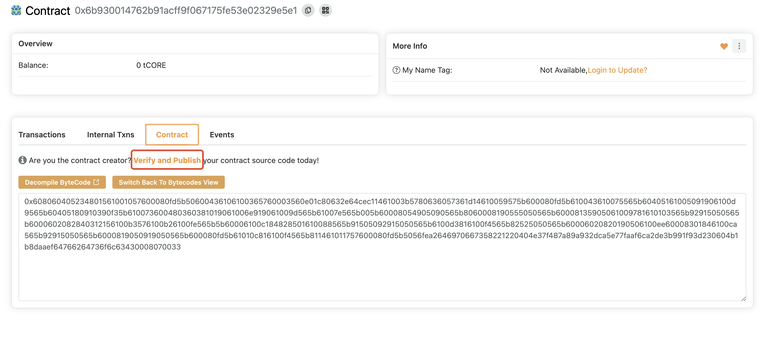
- Fill in the required verification information on the page, specifically:
- Contract address;
- Compiler type: For simple contracts, select the
Single Filecompiler type. For more complex contracts, such as contracts with external imports, choose theStandard Jsoncompiler type. - Compiler version;
- Open-source license type;
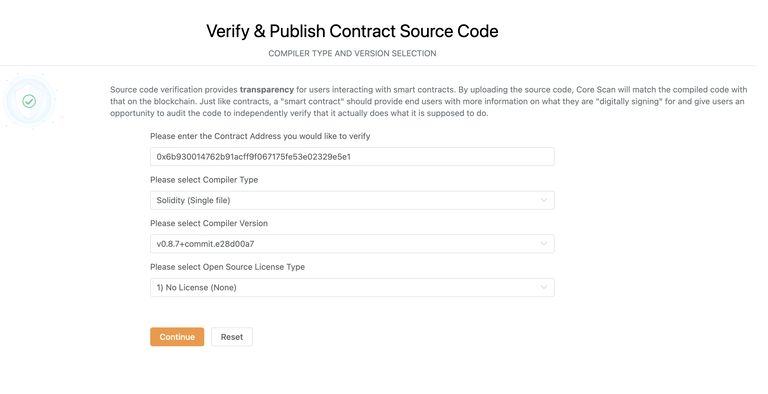
- On the next page, please fill in the Solidity source code for the contract.
If your contract has constructor parameters, it is recommended to specify them in the Constructor Arguments field, although it’s not mandatory. The constructor parameters should be formatted as ABI-encoded bytes. Remix and other tools can generate these for you.
If you enabled optimization during contract compilation, select "Yes" for the Optimization field.
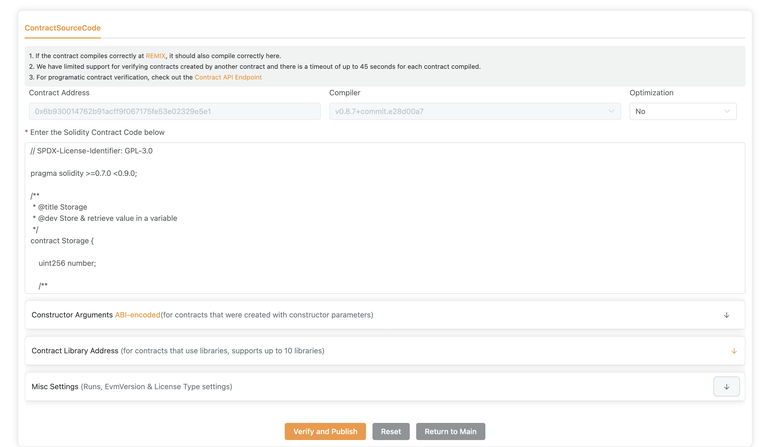
- Click on Verify and Publish to finish the process.
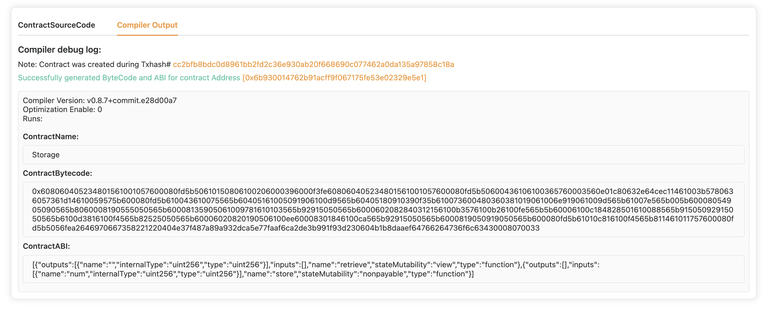
Now your verified contract on Core Scan should look like this:
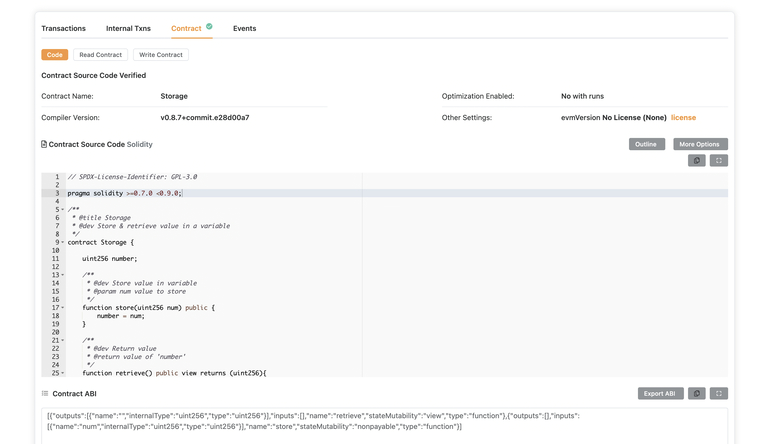
Core REST API Verification
You can find the guide to using the Core API to verify contracts here. Please note that to make API calls, you must register on Core Scan and generate an API key.
If you're familiar with the Etherscan API, you're in luck! The API calls on Core are 100% compatible with the Etherscan API. You just need to replace the API key and endpoint URL, and everything should work correctly.
Hardhat Verification
Hardhat verification is the most convenient way for developers to verify smart contracts. For more information on Hardhat verification, refer to the official Hardhat verification guide located here.
Please note that you’ll need to add Core networks as custom chains, as seen below in a sample Hardhat config:
/**
* @type import('hardhat/config').HardhatUserConfig
*/
const { PrivateKey } = require("./secret.json");
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers");
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle");
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-verify");
module.exports = {
defaultNetwork: "testnet",
networks: {
hardhat: {},
testnet: {
url: "https://rpc.test2.btcs.network",
accounts: [PrivateKey],
chainId: 1114,
},
mainnet: {
url: "https://rpc.coredao.org",
accounts: [PrivateKey],
chainId: 1116,
},
},
etherscan: {
apiKey: {
testnet: "api key",
mainnet: "api key",
},
customChains: [
{
network: "testnet",
chainId: 1114,
urls: {
apiURL: "https://api.test2.btcs.network/api",
browserURL: "https://scan.test2.btcs.network/",
},
},
{
network: "mainnet",
chainId: 1116,
urls: {
apiURL: "https://openapi.coredao.org/api",
browserURL: "https://scan.coredao.org/",
},
},
],
},
solidity: {
compilers: [
{
version: "0.8.24",
settings: {
evmVersion: "shanghai",
optimizer: {
enabled: false,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
],
},
paths: {
sources: "./contracts",
cache: "./cache",
artifacts: "./artifacts",
},
mocha: {
timeout: 20000,
},
};
Foundry Verification
Update the foundry.toml file to specify the Solidity version and EVM version for your project.
[profile.default]
solidity_version = "0.8.24" # Specify the Solidity version
evm_version = "shanghai" #Specify the EVM version
Create an .env file to store sensitive information such as your private key, RPC URL, and API keys. This helps keep your credentials secure and allows you to reference them in your code easily.
RPC_URL = " https://rpc.test2.btcs.network"
PRIVATE_KEY = "YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY"
CORESCAN_API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY"
API_URL="https://api.test2.btcs.network/api"
Important: Never commit this .env file to version control (e.g., GitHub) to prevent exposing your sensitive information. If you're using git, add the .env file to your .gitignore.
Now that you've created the above .env file, run the following command to load the environment variables in the current command line session:
source .env
Execute the below command to verify your smart contract
forge verify-contract 0xContract_Address ContractName --verifier-url $API_URL --api-key $CORESCAN_API_KEY --watch
Replace 0xContract_Address and ContractName with your actual contract address and the contract Name.
Foundry will handle the verification process; you can use Core Scan to search for the contract's address to verify that the contract was successfully deployed and verified.
Known Limitations
- Currently, Core only supports solidity compiler versions up to 0.8.24.
- Libraries are not supported using API verifications.
- If you run into issues verifying very large (1000+ lines) single-file contracts, we recommend switching to
Standard JSONformat for verification.