Core RPCs Through the Command Line
Blockchains generate massive amounts of data, including transaction volumes and asset ownership, which are valuable for decentralized applications (dApps) across the ecosystem. However, accessing and utilizing this data often requires significant technical expertise.
What are Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs)?
Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) help solve this problem by enabling communication between blockchain networks and users, applications, or companies. Instead of setting up a full custom node or complex program to pull data, RPCs allow developers to gather the necessary information by simply accessing the provided endpoint.
Think of an RPC as the reverse of an oracle. While an oracle brings external data (e.g., election results or weather forecasts) into the blockchain, an RPC extracts internal blockchain data (e.g., transaction or block information) and moves it out.
RPC Providers for Connecting to the Core Network Mainnet
The Core supports different RPC providers, both native Core RPC and third-party RPC providers. Refer to the complete list of RPC endpoints here for connecting to the Core mainnet or testnet.
Working with RPCs Through the Command Line
To connect to Core RPC endpoints via the command line, we can use cURL (Client URL). This tool allows developers to fetch data directly from remote servers. The simplest cURL command retrieves a webpage's HTML code by passing in a URL.
Here's an example:
curl https://coredao.org/
To fetch information about a specific transaction on the Core blockchain, use the following cURL command, replacing the transaction hash with your desired value:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST \
--data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getTransactionByHash","params":["0xc9c4a5d14857ace0db197c7393806868824763377f802645aacf6f38d9c309b7"],"id":1}' \
--url 'https://rpc.ankr.com/core'
In the above statement, the following are the components of the curl statement:
- curl: The command to execute the request.
- -H: Specifies the header, in this case, setting the content type to JSON.
- -X POST: Defines the HTTP method to use (
POST). - --data: The request body, including the
method,parameters, andrequest ID. - --url: The endpoint
URLto which the request is sent.
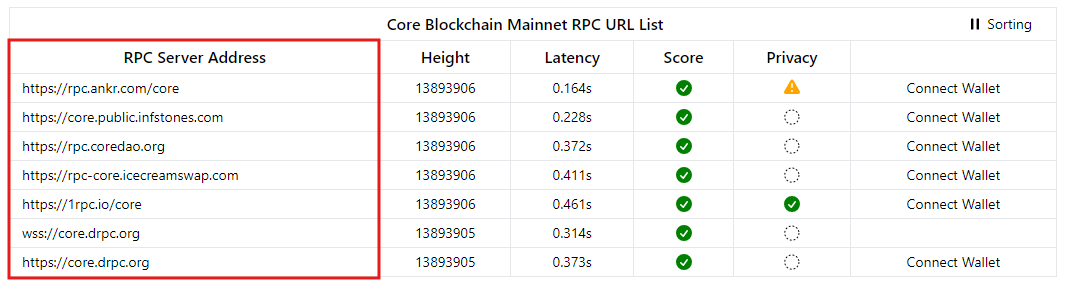
As explained earlier, CURL is a method for sending API requests, which contain an endpoint (i.e., the URL from which the information is being retrieved) and an HTTP method. In our case, the URL comes at the end after the --url option; you can swap in any of the valid RPC URLs found here for connecting to Core Mainnet, just don't forget to wrap the URL in single quotes (''). In the figure below, any of the URLs in the red box will work.
Sample Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"blockHash": "0xb1cbf38843207e6133b69b53559c22c61463208cc2a822a92ba18e30da3054ba",
"blockNumber": "0x972743",
"from": "0x7ef3a94ad1c443481fb3d86829355ca90477f8b5",
"gas": "0x7a120",
"gasPrice": "0x0",
"hash": "0xc9c4a5d14857ace0db197c7393806868824763377f802645aacf6f38d9c309b7",
"input": "0xf340fa010000000000000000000000007ef3a94ad1c443481fb3d86829355ca90477f8b5",
"nonce": "0x74622",
"to": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000001000",
"transactionIndex": "0x4",
"value": "0x2d01fcfa9da000",
"type": "0x0",
"v": "0x8dc",
"r": "0x15c80da30b54e61f383f38f2033f71ef4201a39ff4e799dadf13937dde88b1a0",
"s": "0xd63214598ae5cd8da665517e60d8471f1b4c591711247d0f94958ec0add4ba9"
}
}
Using cURL in a Python Workflow
If you prefer working in an IDE rather than the command line, you can replicate the cURL command using Python’s requests library. Here's how:
import requests
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
}
data = '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getTransactionByHash","params":["0xc9c4a5d14857ace0db197c7393806868824763377f802645aacf6f38d9c309b7"],"id":1}'
response = requests.post('https://rpc.ankr.com/core', headers=headers, data=data)
print(response.content)
You can replace the URL https://rpc.ankr.com/core with any valid RPC URL found in the Core documentation, and don't forget to wrap the URL in single quotes.