Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW)
Overview
Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) introduces an innovative way to incorporate Bitcoin's miners in the security and validator election process of Satoshi Plus consensus—without requiring any additional computation.
DPoW forms a symbiotic relationship between the Bitcoin and Core networks:
- Bitcoin miners gain a second block reward through CORE token rewards
- Core benefits from Bitcoin's unmatched security and decentralized infrastructure
Core Concepts
- No new hardware or mining activity required
- Miners maintain standard Bitcoin mining operations
- Miners delegate their hash power to vote for Core validators via metadata
- Miners earn CORE rewards in addition to their Bitcoin rewards
How DPoW Works
1. Mining Integration
Bitcoin miners continue their usual mining operations. To participate in DPoW, they include delegation metadata in the op_return field of the coinbase transaction. This metadata contains:
- Core Validator Address: The validator the miner is supporting
- CORE Reward Address: Where the miner wants their CORE rewards sent
This process:
- Requires no extra energy
- Does not interfere with Bitcoin mining
- Extends miner protection to the Core network
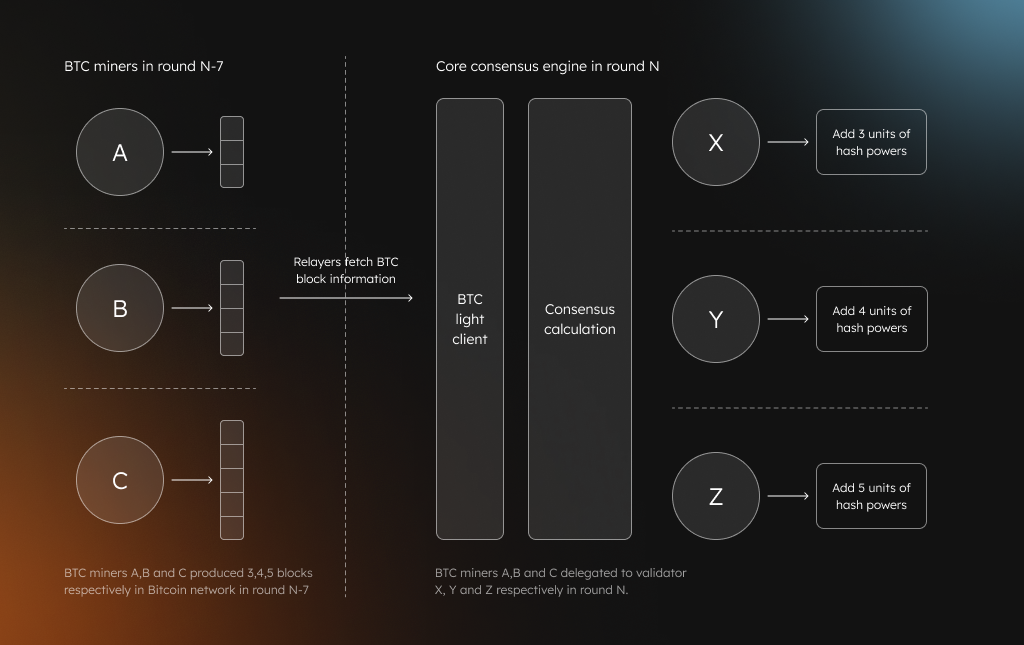
2. Relayers and Data Flow
To capture this delegation information:
- Relayers monitor the Bitcoin blockchain in real time
- An on-chain BTC light client extracts delegation metadata
- Data is sent to the Core Delegation Hub, which:
- Validates the data
- Aggregates delegations
- Assigns weight to validators based on miner hash power
3. Validator Election Process
Every day, Core calculates validator scores using miner delegation data from one week prior. Validators with higher delegated hash power have higher election probability
4. Rewards and Incentives
- Elected validators earn CORE rewards for producing blocks
- Validators take a small commission
- Remaining rewards are passed to delegators (including participating miners)
Outcome: Miners earn both:
- Bitcoin rewards (as usual)
- CORE token rewards (via validator delegation)
Benefits
For Bitcoin Miners
- Earn More: Gain CORE tokens with no added energy cost
- Stay Independent: Continue mining Bitcoin without operational changes
- Diversify Returns: Earn CORE tokens in addition to Bitcoin rewards
For Core
- Bitcoin Security: Integrates real PoW into its validator election
- Decentralized Validator Set: Miners from anywhere can help secure Core
- Ecosystem Alignment: Miner economic interests are aligned with the Core network
Best Practices for Miners
- Select trustworthy Core validators
- Ensure correct metadata in op_return field
- Monitor your CORE rewards address for incoming distributions
- Maintain consistent mining operations to ensure reliable delegation
Potential Challenges & Mitigations
| Challenge | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Incorrect metadata format | Core validates metadata before processing |
| Missed rewards | Use reliable tooling to monitor reward addresses |
| Validator underperformance | Choose validators with strong historical uptime |
Getting Started
To participate in DPoW:
- Continue your Bitcoin mining (no changes needed)
- Embed delegation metadata in op_return of coinbase transaction
- Choose a Core validator to delegate to
- Add your CORE reward address
- Track rewards and validator performance
Why It Matters
DPoW is a critical component within Satoshi Plus consensus. It extends the incentives of Bitcoin miners to align with Core's consensus mechanism. Core receives Bitcoin miner participation in its security, and Bitcoin receives better-compensated miners. The result is a miner set that is more heavily incentivized to secure both Bitcoin and Core.