How Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking Works
CLTV Timelock Mechanism
CheckLockTimeVerify (CLTV) is a Bitcoin-native function that locks transaction outputs until a specified time or block height. When you create a CLTV transaction:
- Bitcoin remains locked in your wallet for the specified duration
- No third party can access your Bitcoin during the lock period
- You retain full custody throughout the entire process
- After expiration, you must send a redeem script to regain spending ability
Staking Process Overview
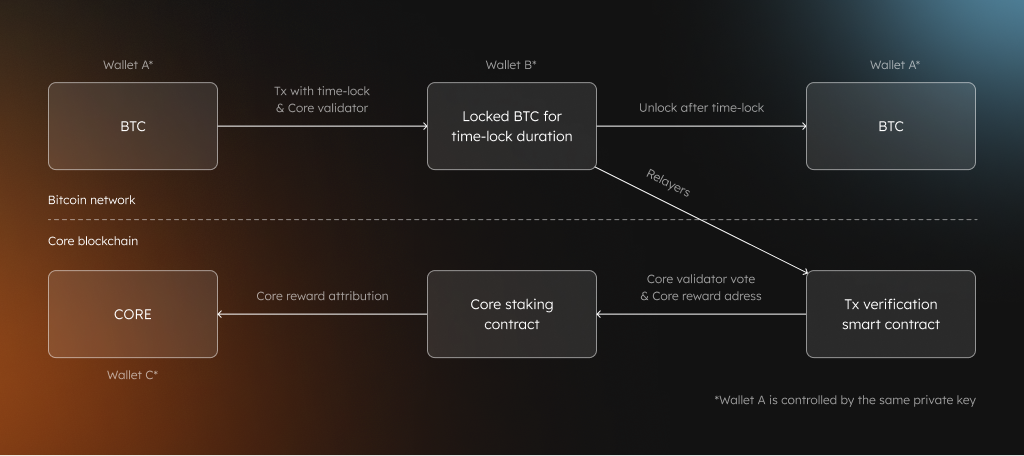
- Create timelock transaction with CLTV on Bitcoin blockchain
- Include metadata specifying validator delegation and reward address
- Core relayers detect valid staking transactions on Bitcoin
- Earn CORE rewards based on validator performance and staked amount
- Redeem Bitcoin after timelock expires using redeem script
Security Model
Zero Custodial Risk: Your Bitcoin never leaves the Bitcoin blockchain or your control. The staking mechanism uses only Bitcoin-native functions without introducing additional trust assumptions.
Key Security Guarantees:
- Bitcoin remains in your wallet throughout staking
- No protocol-level risk beyond Bitcoin's native security
- No third-party custody or smart contract risk
- Validator misbehavior cannot affect your Bitcoin principal
Technical Requirements
Transaction Structure
Your CLTV staking transaction must include:
Required Outputs:
- CLTV timelock output: Locks your Bitcoin for specified duration
OP_RETURNoutput: Contains delegation metadata
Metadata Format (in OP_RETURN):
- Core validator address (delegation target)
- CORE reward address (where to send rewards)
Minimum Requirements
| Method | Minimum BTC | Minimum Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Official UI | 0.01 BTC | 5 days |
| Direct scripting | No minimum | 24 hours (recommended) |
Cross-Chain Operations
| Step | Bitcoin Network | Core Network |
|---|---|---|
| Initiate | User creates CLTV transaction with delegation metadata | Relayers monitor for valid staking transactions |
| Timelock | Bitcoin locked in user's wallet, transaction confirmed | Relayers validate and register staking position |
| Earn | Bitcoin remains locked and secure | CORE rewards accrue based on validator performance |
| Redeem | User sends redeem script to unlock Bitcoin | Relayers update staking records |
Transaction Workflow
Timeline and Activation
Confirmation Process
- Transaction broadcast: CLTV transaction sent to Bitcoin network
- Bitcoin confirmation: ~60 minutes (6 blocks) for recognition
- Core detection: Relayers identify valid delegation
- Reward activation: Next validator election round (~24 hours from UTC+0)
Example Timeline If you stake Bitcoin at 6:00 AM UTC+0:
- Bitcoin confirmation: Same day after 6 blocks
- Staking becomes active: 12:00 AM UTC+0 next day
- Rewards begin accruing: From first active round
Best Practices
Transaction Fees
- Use competitive fees: Low fees cause confirmation delays
- Monitor network congestion: Adjust fee rates accordingly
- Consider RBF: Enable Replace-By-Fee for fee adjustments
Handling Delays
- Transaction accelerators: Use services like viaBTC if stuck
- Fee bumping: Increase fees on pending RBF transactions
- Patience: Low-fee transactions may take days during congestion
Validator Selection
Choose validators based on:
- Performance history and uptime
- Commission rates
- Community reputation
Redelegation vs Redemption
Redemption: Unlock Bitcoin for general use
- Requires redeem script after timelock expires
- Bitcoin becomes fully spendable again
Redelegation: Switch to different validator without unlocking
- Can be done directly without redemption
- Maintains staking position with new validator
API and Data Access
Staking data becomes available via Core Staking API once:
- Bitcoin transaction is confirmed (6 blocks)
- Relayers have processed the delegation
- Staking position is active in validator elections
This allows developers to track staking positions, rewards, and validator performance programmatically.
For a detailed guide on staking transaction design, refer here.